Recently, Prof. Xiao Zhubing's research group (Henan Key Laboratory of Photovoltaic Materials) of Henan university made important progress in the research on high volumetric energy density Li-S battery. This original research paper entitled "Selective S/Li2S Conversion via in-built Crystal Facet Self-mediation: Toward High Volumetric Energy Density lithium-sulfur Batteries” was published in the international top journal ACS Nano (IF 14.588). Henan university is the only corresponding address for this work. Paper link: https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c04933
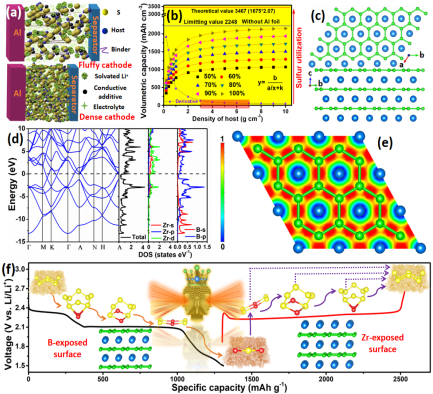
Lithium–sulfur (Li–S) batteries, which are able to provide a much higher energy density (2600 Wh kg−1) compared to that of Li-ion batteries (≈300 Wh kg−1), have received increasing interest in recent years. Despite possessing advantages, such as natural abundance and multiple valence states which lead to a high capacity, the low electronic conductivity of sulfur, the shuttle effect of soluble Li2Sx (3 ≤ x ≤ 8, known as polysulfides), and the volume expansion have greatly limited the use of Li–S batteries in practical applications. Xiao’s group developed a eutectic salt-adjuvant solid-phase synthesis method to fabricate graphene-like metallic ZrB2 nanoflakes with high tap density at a relatively low temperature. An in-built Janus crystal facet self-mediation behavior for Li-S electrochemistry is confirmed on the local exposed B and Zr sites with combined first-principle calculations and spectroscopic studies, in which the negative charged B sites mainly mediate the discharge process, while the positive charged Zr atoms enable a further oxidation of the prefixed LiPS to the end product S during charging, ensuring high sulfur utilization even at high current densities and high sulfur loading. Unlike previous strategies to trap LiPS by non-specific mediation behaviors, this selectively catalytic property for Li-S electrochemistry is quite efficient. The resultant ZrB2-S electrode delivers a high cell-level volumetric energy density of 533 Wh L-1. High volume energy density and long cycle performance of Li-S batteries are realized by self-mediation of ZrB2 in-built crystal facet in the charging and discharging process, which makes the application of Li-S battery a solid step further.
This work was financially supported by the Scientific Research Foundation for “Special Support Program for Exceptional Talents” of Henan University. Dr. Tianli Wu and master student Jing Qi are the co-authors. Prof. Zhubing Xiao is the only corresponding author.

 Research /
Research Achievements /
Science & Technology /
Key Laboratory of Photovoltaic Materials /
Content
Research /
Research Achievements /
Science & Technology /
Key Laboratory of Photovoltaic Materials /
Content


