Recently, Dr. Yajie Tian (School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, HENU), Professor Yong Zhao (School of Materials Science and Engineering, HENU), and Professor Guozhu Liu (School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University) report new progress in preparation and application of zeolite catalysis. The relevant paper achievement is published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition entitled "Template Guiding for encapsulating of Subnanometric Platinum Clusters in Beta-Zeolites Enabling High Catalytic Activity and Stability" (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202108059).
Sub–nanometric metal clusters show unique and unexpected properties because of coordinatively unsaturated surface atoms, resulting in excellent catalytic performance in reactions like water–gas shift, alkane dehydrogenation and selective hydrogenation reactions. However, the clusters always suffer from serious aggregation because of their high surface free energy under harsh synthesis or reaction conditions, resulting in low catalytic activity and selectivity. Encapsulation of metal clusters within zeolites provides the great opportunity to inhibit the metal aggregation, in which the metal clusters may interact with zeolites framework to prevent their coalescence, and the dimensions of metal clusters can be controlled by the spatial constraints of the zeolite channels. It is highly desirable to develop a general and efficient strategy for encapsulating subnanometric metal clusters in zeolite regardless of the Si/Al molar ratio, which would confer enhanced catalytic activity and stability in various reactions.
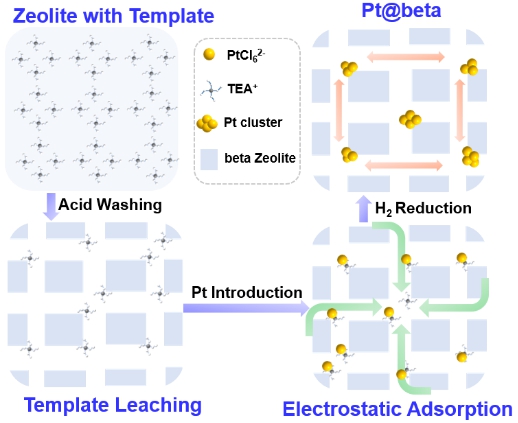
Scheme 1. Template–guidance approaches for the encapsulation of metal clusters within zeolites
This work report a new template–guidance approach for encapsulating metal clusters in zeolite (Scheme 1). The as–synthesized zeolite is treated by acid to leach part of the template for generation of transport pathway for metal ions. Owing to the electrostatic interactions of negatively–charged metal ions on positively–charged template agents, single–atom distribution of metal within the zeolite is realized. Sequenced by direct reduction in pure H2, the encapsulation of sub–nanometric Pt clusters of a narrow size range in intersectional sites of the zeolite (Pt@beta) is achieved. Compared to the general top–down and bottom–up strategies, the proposed template–guidance approach uses template as a metal anchoring agent stabilizing Pt metal ions, which is regardless of aluminum content. Templates as metal protective agents can stabilize Pt metal ions in zeolite during its synthesis procedure, which are gradually decomposed with generation of metal–zeolite interaction. The uniformly dispersed Pt clusters interacting strongly with oxygen in zeolite framework of Pt@beta, exhibited enhanced activity and stability in hydrodeoxygenation reactions (Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2021, DOI: 10.1002/anie.202108059).
In this work, Dr. Yajie Tian (School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, HENU) is the First Author, Professor Guozhu Liu (School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University), and Professor Yong Zhao (School of Materials Science and Engineering, HENU) are Co-corresbonding Authors. Financial supports by National Natural Science Foundation of China, Technology Research Project of Henan Province and the “First–Class" Discipline Construction Project of Henan University.

 Research /
Research Achievements /
Science & Technology /
School of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences /
Content
Research /
Research Achievements /
Science & Technology /
School of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences /
Content


