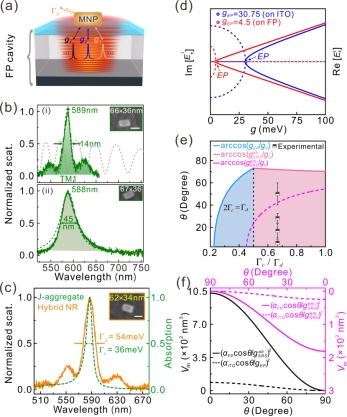
Realizing the single-exciton strong coupling with localized plasmon mode (LPM) at room temperature is highly desirable for exploiting quantum technology. However, its realization has been a very low probability event due to the harsh critical conditions, severely compromising its application. To overcome this challenge, Prof. Renming Liu cooperating with Xue-Hua Wang’s research group present a highly-efficient approach for achieving such a strong coupling by reducing the critical interaction-strength at the exceptional point based on the damping inhibition and match of the coupled system, instead of enhancing the coupling strength to overcome the system’s large damping. Experimentally, they compress the LPM’s damping linewidth from ~45 nm to ~14 nm, using a leaky Fabry–Perot cavity, a good match to the excitonic linewidth of ~10 nm. It dramatically relaxes the harsh requirement in mode volume by more than an order of magnitude and allows the maximum direction angle of the exciton dipole relative to the mode field up to ~71.9°, significantly improving the success rate of achieving the single-exciton strong coupling with LPM from ~1% to ~80%, which will greatly boost an advance in room-temperature quantum devices.
The related paper entitled with "Highly Efficient Single-Exciton Strong Coupling with Plasmons by Lowering Critical Interaction Strength at an Exceptional Point" has been published in Physical Review Letters. Dr. Wei Li is the first author, Prof. Renming Liu and Prof. Xue-Hua Wang are the corresponding authors. The research work is supported by the National Key R&D Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundations of China, the Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province, and the Guangdong Special Support Program.
Link to this paper: https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.130.143601

 Research /
Research Achievements /
Science & Technology /
School of Physics and Electronics /
Content
Research /
Research Achievements /
Science & Technology /
School of Physics and Electronics /
Content


